Tire Talk: Supply Chain Challenges in Tire & Rubber Industry
The tire and rubber industry focuses on influence and brand loyalty, the capital needed to modernize manufacturing methods, and maintaining advanced research and development facilities. The high demand for industrial and agricultural vehicles drives the need for tire and rubber products. To meet demands, tire manufacturers oversee the significant factors that affect the demand for tires as products, including the re-treading of tires, transportation volumes, logistics network, and execution of vehicle loading rules and exports. The goal remains to develop affordable, efficient, and durable tires at affordable prices while meeting sustainability goals. But what goes behind the wheel remains unseen. How difficult has it been for the industry to manage shorter order-to-delivery cycles, achieve reduced operating costs, enable an efficient logistics network, and meet sustainable goals?
This blog discusses the key supply chain challenges tire manufacturers face and how Quloi helps you implement long-term solutions that are resilient and effective to unforeseen disruptions in the tire and rubber supply chain.
Tire and Rubber Supply Chain Challenges
Raw materials are scarce, skilled labor is increasingly hard to find, sustainability comes at a price, consumer preferences are changing, and technology is evolving. In short, supply chain challenges have been catapulted to the top of the tire and rubber industry as globalization and tech rule around. Some of the common challenges are discussed below:
Raw Material Sourcing
Asia prominently holds 90% of the world’s natural rubber market share, with Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Vietnam accounting for about 70% of the global natural rubber production. The Southeast Asia region has created a favorable ecosystem for tire manufacturing; however, climate change, political tensions, and bacterial diseases like leaf blight disrupt the supply. Natural rubber trees require specific climatic conditions, and bad weather conditions can significantly threaten yield, disrupting the supply chain. On the other hand, synthetic rubber production relies on fossil fuels as a raw material and an energy source for manufacturing processes. According to the USA Tire Manufacturers Association, passenger and truck tires account for 24% and 11% of synthetic polymers, respectively, in the life of a tire. The chemical-intensive nature of synthetic rubber production can result in detrimental effects on environmental health and human well-being.
Transportation and Logistics
Timely deliveries have become a dire customer need and spurred road transportation traffic. However, global shipping constraints like container shortages, port congestion, and geopolitical instability interrupt last-mile deliveries by causing significant delays – resulting in increased lead times and costs. With even pre-booked cargo shipments, companies are experiencing about one month of delays. This disruption will be starkly reflected in the likely increase in rubber prices in the Indian market, with the current price of RSS 4 rubber at INR 203 per kg. The global container shortage, spot freight rates soaring around 105%, and ongoing port congestion leave a cascading effect on the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Tire makers are pressured to transition to cleaner technologies as regulators scrutinize tire pollution. Tire pollution is set to surge with the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). The high turnover rate of car tires generates considerable waste with limited ways for closed-loop recycling. This has resulted in alternative recycling methods for ELTs, e.g., infill on artificial sports fields, of which approximately 21% of ELTs are recycled in Europe. The latest risk assessment by EU authorities found that this form of recycling method results in 16,000 tonnes of microplastics annually, posing significant environmental risks.
Quality Control
Maintaining consistent quality control throughout the supply chain is vital for the tire and rubber industry. Variations in the quality of natural rubber due to differences in climate, harvesting techniques, and regional practices can impact the final product’s performance and safety. Ensuring uniform quality requires stringent quality control measures and reliable supplier relationships. However, dependence on a limited number of suppliers for critical materials increases the risk of supply chain disruptions. Manufacturers must diversify their supplier base while maintaining high-quality standards, a challenging task that requires rigorous vetting processes and ongoing supplier assessments.
Technology Integration
Integrating advanced technologies into the supply chain can enhance efficiency and visibility but also presents significant challenges. Implementing robust IT systems that can handle vast amounts of data from various points in the supply chain is complex and costly. Automation and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies can improve operational efficiency and real-time monitoring, but they require substantial upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. The integration process can be disruptive, demanding an upgrade in existing workflows and staff training.
Economic Factors
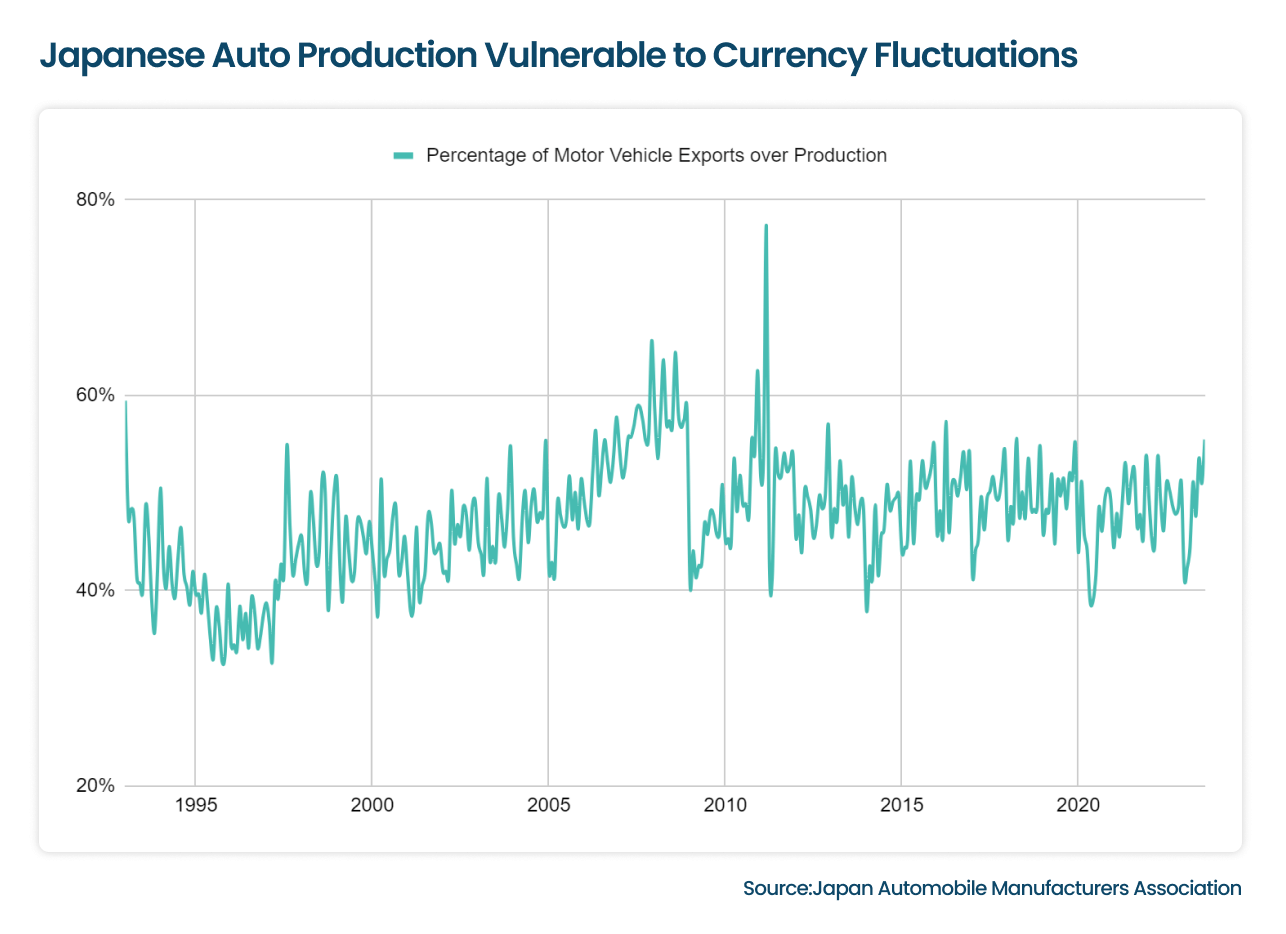
Economic factors, such as currency fluctuations and market demand, significantly impact the tire and rubber industry. As a global sector, the industry is susceptible to currency fluctuations that can affect the cost of imports and exports. For instance, between January 1993 and August 2023, Japan exported about 47% of the motor vehicles (including cars, buses, and trucks) it produced each month. However, currency fluctuations pose a significant challenge for tire manufacturers. Almost half of the Japanese motor vehicle production is exported. If the yen depreciates against other currencies, Japan will see increased demand, boosting exports.
Conversely, Japanese tires will become more expensive if the yen strengthens, and exports will decline. This volatility makes it challenging for tire and automakers to plan production, manage costs, and maintain stable relationships with international clients. The uncertainty of currency fluctuations makes auto production vulnerable, disrupting supply chains and impacting profitability.
Sustainability
There is an increasing pressure to source materials sustainably, limiting options and increasing costs. Sustainable practices, such as ensuring fair labor practices and environmental stewardship throughout the supply chain, present challenges and opportunities. These initiatives require a significant investment and a commitment to ethical practices, which can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. A survey showed staggering statistics for tires and other auto components that account for three-quarters of all rubber demand in the EU. 65% of end-of-life tires (ELTs) are in landfills, while 17.5% go for incineration. Balancing sustainability goals aligned with economic viability remains a complex challenge for manufacturers.
Risk Management
Natural disasters, pandemics, and other unforeseen events can cause significant disruptions, highlighting the need for comprehensive disaster preparedness strategies. Achieving end-to-end visibility in the supply chain helps anticipate and mitigate risks. This requires investment in advanced tracking and monitoring technologies, enabling tire and rubber manufacturers to identify potential issues before they escalate.
Looking Ahead: Scaling Success with Quloi
The tire and rubber supply chain is plagued with challenges that significantly impact its efficiency and profitability. High raw material costs, which comprise approximately 32% of the total production expense, continue to stress tire manufacturers. These costs are exacerbated by geopolitical concerns, timely and accurate delivery, advanced technologies, environmental issues related to emissions and hazardous waste produced during manufacturing, and a limited supply of critical raw materials, such as synthetic and natural rubber, contributing to rising production costs and market instability.
While the tire and rubber supply chain will remain vulnerable to disruptions, maintaining their hard-won seat at the top table will remain a key task for supply chain leaders. Though it cannot be predicted exactly when big shocks will occur in the industry, Quloi can help you assess the severity of their impact. The cloud-powered supply chain visibility and collaboration software, Quloi, helps you leverage an expert approach that can change the supply chain game for tire manufacturers. How?
- Monitor the status of tire and rubber orders in real-time.
- Track shipments across road, air, and ocean routes.
- Strengthen collaboration with freight forwarders to optimize logistics.
- Integrate seamlessly with existing ERP systems to eliminate data entry errors.
- Utilize dedicated workspaces to enhance productivity and accountability among tire supply chain teams.
- Simplify logistics planning and minimize lead times for tire and rubber shipments.
- Integrate with Slack and Microsoft Teams for seamless communication and quick decision-making.
Maximize the potential of the tire and rubber supply chain with Quloi’s FREE One-on-One Expert Consultancy. Benefit from our experienced consultant and take expert technical guidance for effective supply chain management in the tire and rubber industry.
Related Articles


