Enabling Data Security Solutions for Digital Supply Chains
You can keep your company data hidden as securely as possible against digital invaders and still be at risk from online cybercriminals deep inside one of your supplier’s or vendor’s systems – or one of their suppliers’ or vendors’.
If your organization hasn’t faced a supply chain breach yet, consider yourself one of the lucky few. According to a Gartner report, around 89% of organizations have been impacted by a data breach at a supplier in the last five years. No organization is immune and has a complete mitigation plan for supply chain disruptions. That, however, is not an excuse for improved readiness and enhanced competitiveness through well-designed supply chain strategies.
What supply chain security challenges might your organization face? What common threats are there? How can you prevent potential attacks and enable a secure supply chain?
This blog has all the answers you need. Read this blog post to understand common supply chain vulnerabilities, why data security is essential, and which practices help improve the security of your supply chain and your resilience to potential cybersecurity attacks.
Importance of Data Security in Supply Chain
Common challenges frequently plague the supply chain, such as fraudulent activities, counterfeiting, fragmented collaboration, and a lack of transparency. The proliferation of counterfeit activities in the marketplace leads to financial setbacks and harm to organizations’ reputations. The intricate nature of modern supply chains exacerbates these issues, making it challenging to oversee every movement effectively. According to the latest report, the global average data breach cost is $4.88 million, which has increased by 10% in one year – the biggest jump since the pandemic. Business disruption and post-breach response activities led to an increase in cost.
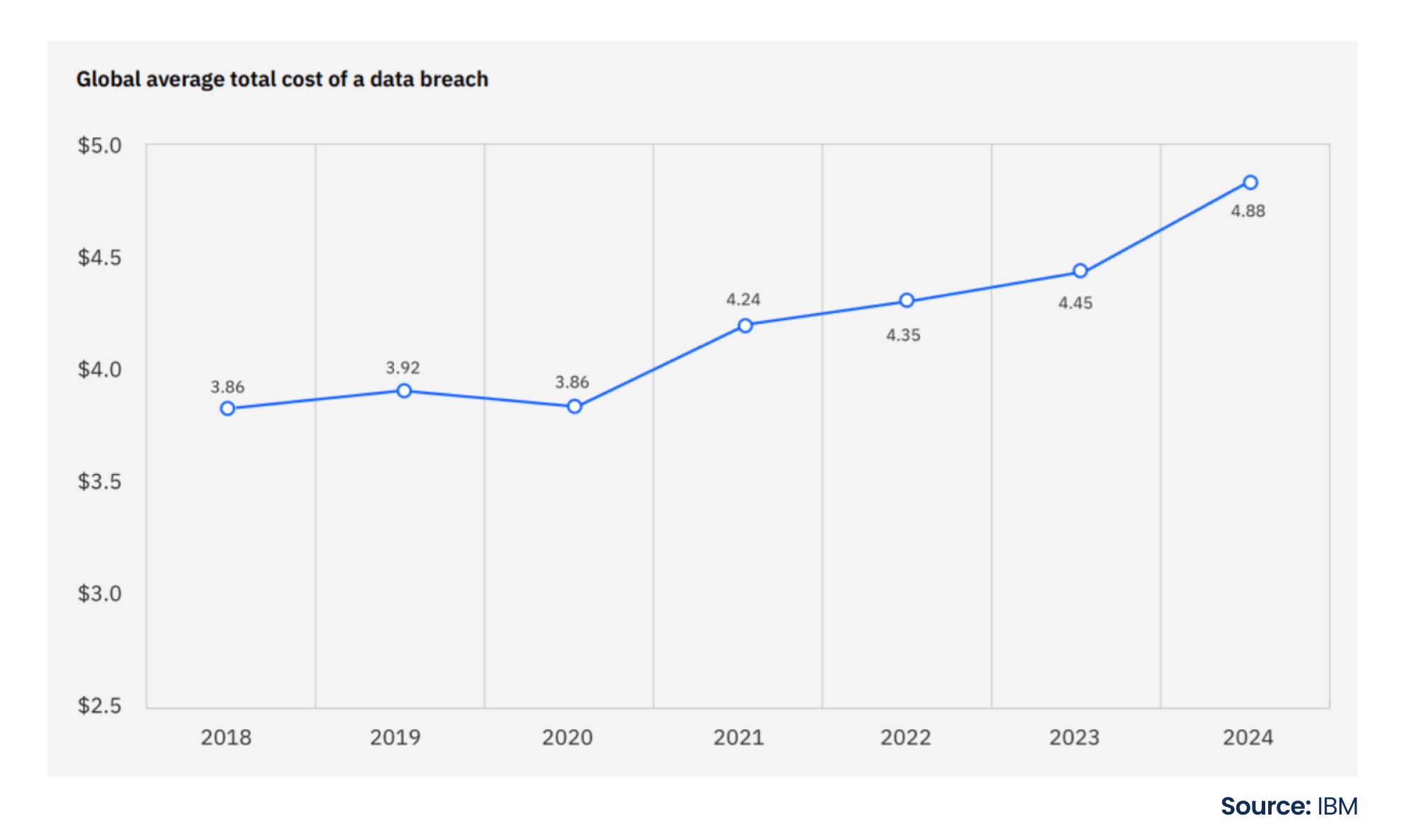
Customers, partners, and key stakeholders expect their data to be handled responsibly and securely. Adherence to data protection regulations is essential to avoid financial consequences and maintain customer trust. For instance, under the GDPR, organizations can face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their annual global turnover, whichever is higher, for violating security standards. Also, according to the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), organizations can face penalties of up to $2,500 per unintentional violation, up to $7,500 per intentional violation, or those involving minors.
That’s when data security becomes a laser-focused area in the supply chain to protect valuable information, control high costs, and preserve business continuity. Improved data security in the supply chain helps reduce the risks of cyberattacks and protect against compromised data, lost products, product downtime, lost proprietary information, and loss of consumer loyalty & trust.
Understanding Security Risks in Supply Chain
As digital technologies and interconnected global networks of partners, vendors, clients, and subsidiaries become a common organizational practice, the potential for cyber attackers to find a security lapse through which they can wag far enough to access sensitive information or disrupt the vendor’s entire ecosystem has become a pressing concern. Understanding supply chains’ common security risks is imperative to develop effective mitigation strategies.
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access: A business functions on data. When data is breached, business gets disrupted. These disruptions can vary from minor breaches that affect only a few systems to severe, organization-wide operational shutdowns. A study found that 70% of organizations experienced a significant or very significant disruption to business resulting from a data breach. Only 1% described their level of disruption as low. The study further showed the severity of a business disruption correlated with data breach costs. Average breach costs were higher when business disruption was greater. Even organizations that reported low levels of disruption faced substantial average data breach costs of $4.63 million. While organizations experiencing significant disruptions incurred higher average costs of $5.01 million, 7.9% higher. In other news, Bank of America reported a ransomware attack targeting Mccamish Systems in February 2024, affecting over 55,000 customers. Forbes stated that the breach involved unauthorized access to personal data, including names, phone numbers, account numbers, addresses, social security numbers, and credit card information.
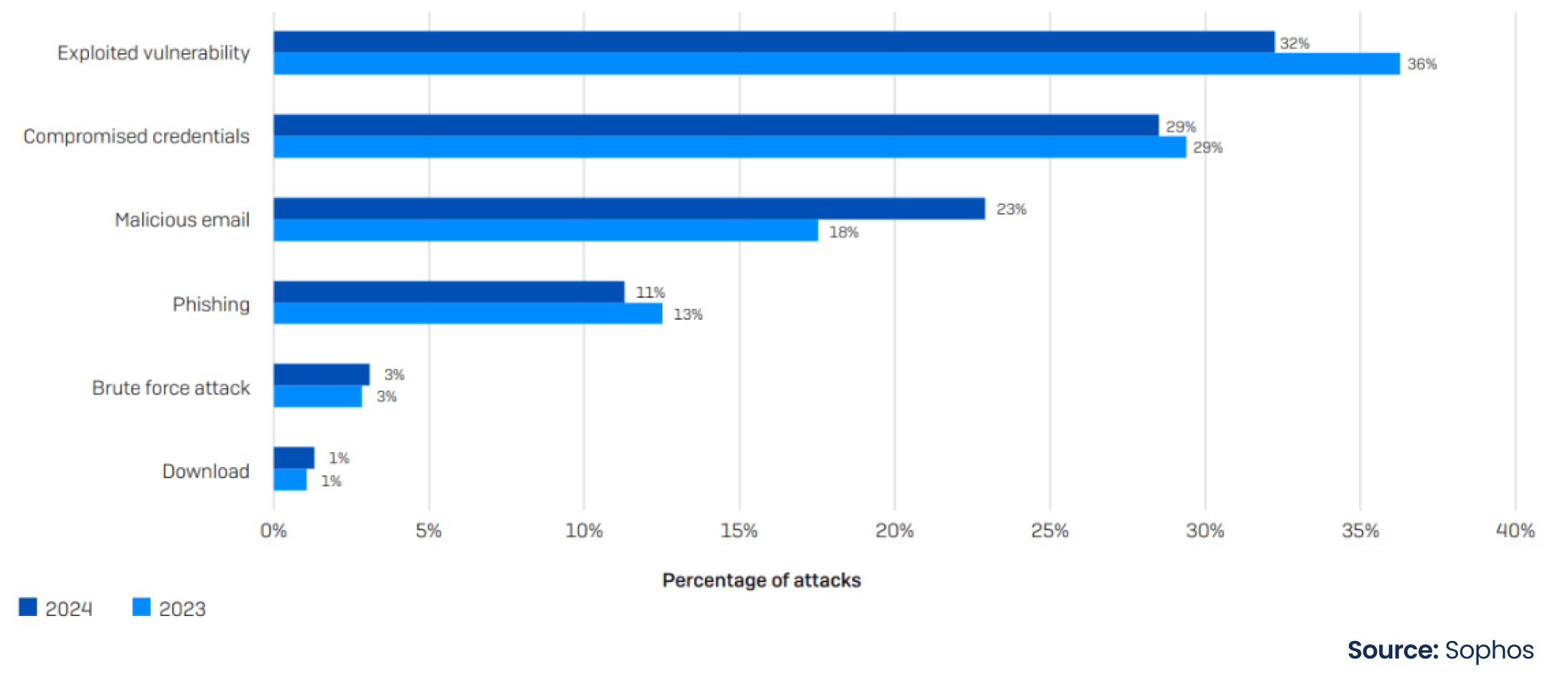
Ransomware Attacks: Supply chains are vulnerable to ransomware attacks due to their increasing reliance on digital platforms and timely data exchange. A survey cited that 59% of organizations were hit by ransomware in 2024, a small but welcome drop from the 66% reported in the previous two years. 34% of organizations identified email-based approaches as the root cause of the attack, with malicious emails (messages with a malicious link or attachment that downloads malware) being twice as common as phishing (messages designed to steal information). While all ransomware attacks have a negative impact, some are more devastating than others. Organizations attacked due to unpatched software vulnerabilities suffered much worse than when the attacker used compromised credentials. 71% of companies attacked through vulnerabilities paid the ransom, while only 45% paid when the attacker used stolen passwords.
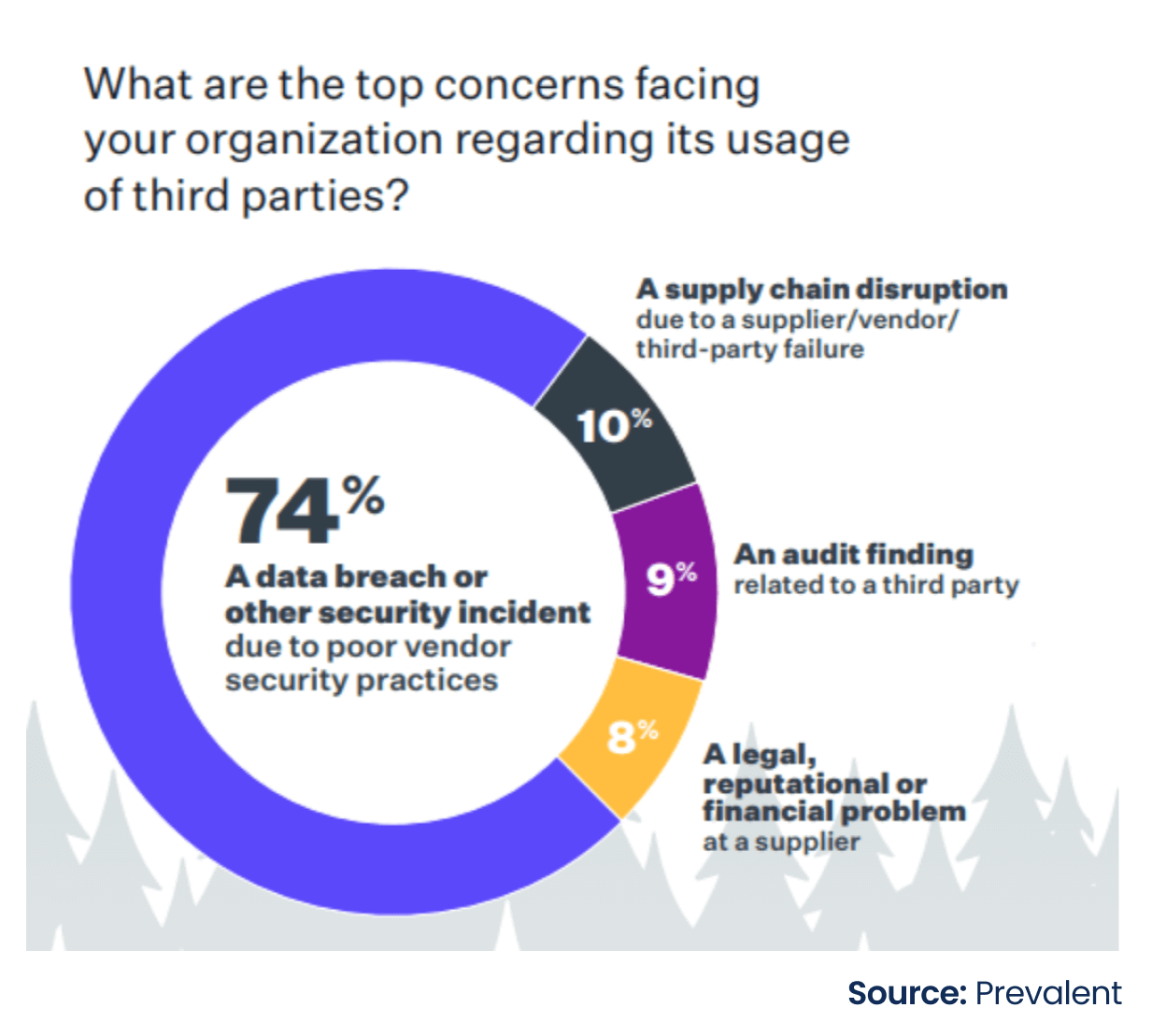
Third-Party Vendor Risks: The size of third-party risks increased to record levels in 2023. Some of the most impactful third-party breaches and software supply chain intrusions were reported last year. Despite a strong emphasis on managing third-party cybersecurity risks, 61% of companies cited a third-party data breach or security incident in the last 12 months – a 49% increase over last year. Further, the report features top concerns facing organizations regarding third-party vendor usage.
Supplier Fraud: Supplier fraud, or vendor fraud, occurs when a cybercriminal claims to be a legitimate supplier and attempts to change payment processes or gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. These attacks often involve advanced social engineering techniques, such as AI-generated voicemails, phishing attacks, and deepfake video recordings. During phishing attacks, it’s your actual suppliers who miss out on owed payments. 323,972 internet users experienced phishing attacks in 2021. This figure indicates that half of the users who fell victim to data breaches were targeted through phishing attacks. Moreover, the financial repercussions of supplier fraud distort businesses. On average, American companies lose $300,000 annually due to fraudulent invoices.
Key Components of Data Security
Supplier Risk Management
Effective supplier risk management is essential to protect sensitive data within the supply chain. This starts with thorough due diligence on suppliers’ data security measures, certifications, and compliance with industry standards. Organizations can form a robust data protection framework by establishing contractual agreements outlining data security requirements. These requirements should encompass confidentiality obligations, data handling protocols, and incident reporting procedures. Reviewing and monitoring suppliers’ security measures ensures ongoing compliance and helps address potential third-party risks associated. A BlackBerry survey reveals that over 75% of organizations have faced cyberattacks targeting their suppliers, underscoring the importance of proactive risk and supplier management.
Data Encryption
Implementing robust encryption mechanisms is a key to securing sensitive information throughout its lifecycle. Encryption techniques are helpful for data transmission and storage, such as leveraging secure protocols like SSL/TLS for data in transit and robust encryption algorithms for data at rest. This helps users ensure that information cannot be deciphered without the encryption key, even if encrypted data is gained unauthorizedly. According to the IBM survey, organizations that use encryption can minimize the financial impact of a data breach by over USD 220,000.
Access Controls
Every click in the supply chain leaves a digital footprint easily accessible to anyone in the digital world. Enforcing strict access controls is important to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing confidential information. This includes enabling role-based access controls (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) that grant permissions based on job roles and responsibilities. Based on a Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) report, organizations implementing MFA saw a 99% reduction in account compromise incidents, highlighting its potential and effectiveness in enhancing security.
Emerging Technologies
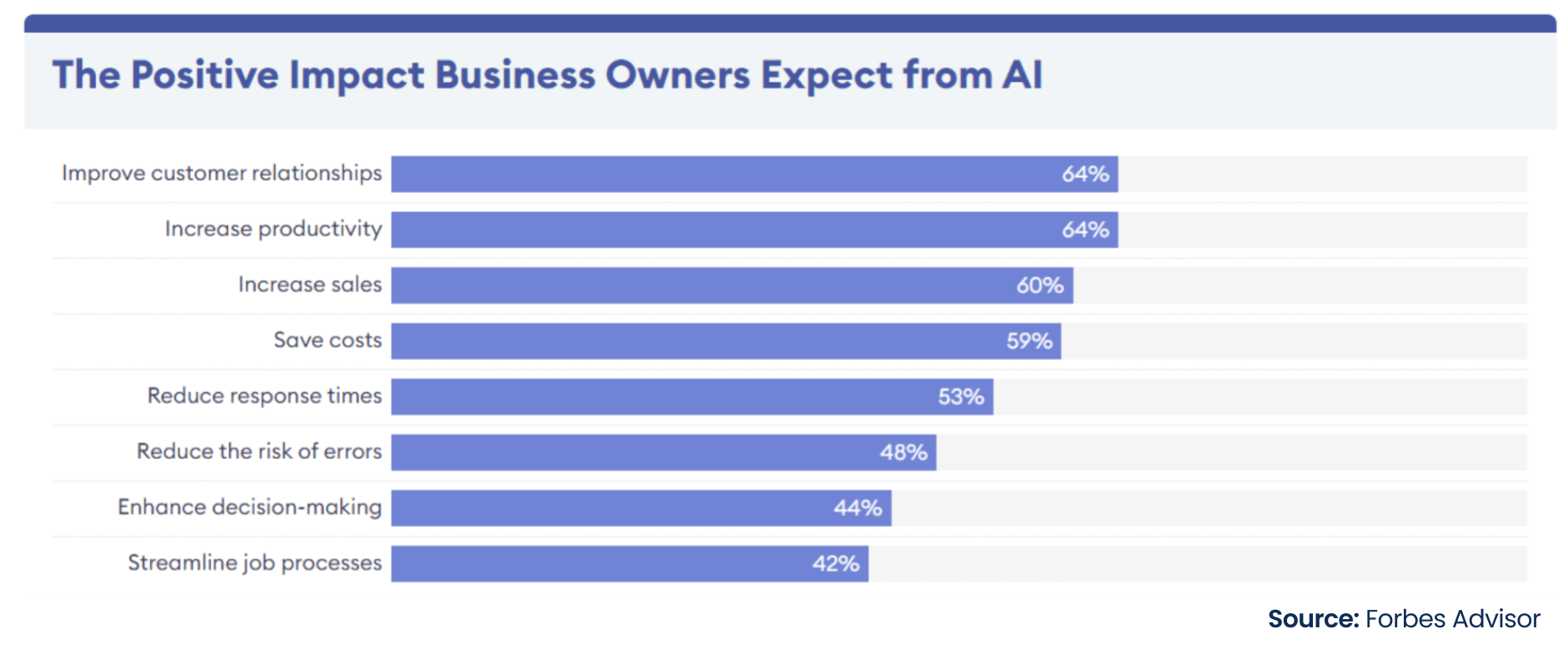
AI, ML, and Blockchain transform data security by enabling real-time threat detection and automated responses. According to the Forbes Advisor survey, organizations leverage AI for inventory management, customer relationship management, digital personal assistants, and content production. Businesses also leverage AI for product recommendations, accounting, supply chain operations, recruitment, and talent sourcing. Most business owners perceive AI as an asset for improved decision-making, optimized lead times, and more. (See Figure below)
Beyond Technology
Human error remains a leading cause of data breaches. Regular training and fraud awareness programs are essential to educate employees about cybersecurity practices like identifying phishing attempts, creating strong and unique passwords, and reporting suspicious activities. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, organizations with fraud-awareness training programs see 50% fewer data breaches than those without. With regular training sessions, you can promote a culture of security awareness and responsible data handling.
Quick Incident Response
There is no denying that data breaches are expensive in an organization’s pockets. When organizations find themselves weighed down with multimillion-dollar costs, they may look to recover those costs elsewhere. Therefore, companies must have a well-designed incident response plan with stringent communication protocols to minimize damage and contain supply chain vulnerabilities. By investing in response preparedness, organizations can reduce data breaches’ disruptive and costly effects while preserving their relationships with partners, customers, and other key stakeholders.
How Can You Leverage Quloi’s Expertise
Predicting how adversaries compromise your organization to launch a cyber attack is difficult. Equally difficult is analyzing the likelihood your organization will be hit and the business ramifications you will face. While you can’t control business disruptions caused by cyberattacks, you can leverage Quloi’s expertise to minimize the impact of supply chain risk and ensure cyber security in supply chain management. Quloi, a cloud-based supply chain visibility and collaboration platform, enhances data security by enabling secure and real-time visibility of purchase orders, booking, and shipment statuses. Quloi’s integration with existing ERP systems maintains data consistency while reducing risks associated with manual data entry. Additionally, platform features like centralized workspaces, role-based access controls, and actionable notifications ensure that sensitive and confidential information is shared securely and only with authorized stakeholders, minimizing the likelihood of data breaches and maintaining supply chain integrity.
Read the whitepaper in the next series to learn more about data security solutions and how you can keep your supply chain secure and resilient.
Interested to learn more? Book a FREE Demo!
Related Articles


