Resolving Automotive Supply Chain Issues for a Brighter Future
The US car and automobile manufacturing market is worth over $104.1 Billion. Over the years, the US car industry has been a hub of innovative production. The industry has changed. It went from Henry Ford’s groundbreaking assembly line to embracing automation and robotics. It also integrated advanced materials and technologies. Even so, car-making processes are evolving. This creates supply chain challenges in the automotive industry due to external factors. These factors force vehicle makers to rethink their practices to address automotive supply chain challenges and find sustainable solutions.
Importance of the Automotive Supply Chain
The global automotive supply chain plays a crucial role in the success and sustainability of the automotive industry. According to research, the US auto industry accounts for 3% of America’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employs over 1.7 billion people in sectors like manufacturing, engineering, design, and the sale of new motor vehicles. It is estimated that the automotive industry could create upto $1.5 trillion or 30% in additional revenue in 2030, compared with about $5.2 trillion from traditional car sales and aftermarket goods/services, up by 50% from about $3.5 trillion in 2025.
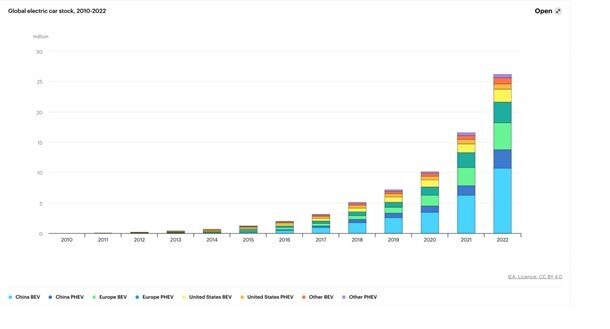
The automotive industry increasingly finds itself at the forefront of technological innovation. To seamlessly integrate these technologies, a well-functioning supply chain becomes all the more critical. The automotive supply industry plays a vital role in the production of electric vehicles (EVs), advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and autonomous driving technologies. Over the span of five years (2017-2022), global EV sales jumped from around 1 million to more than 10 million. In the first quarter of 2023 alone, over 320,000 electric cars were sold in the US, representing a 60% surge from over sales in Q1 2022, underscoring a growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions.
An IEA (International Energy Agency) chart shows the exponential growth of electric cars globally since 2010:
Complexity and Interdependence of the Automotive Supply Industry
The automotive industry is a complex ecosystem of interconnected suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. These stakeholders work closely to ensure the timely production and delivery of cars to customers. The complexity and interconnected dependencies arise from several factors varying lead times, quality standards, and geographical considerations. The automotive supply chain operates on a multi-tiered structure, where each tier depends on the other for interconnected components. These components include Manufacturing and Assembly Processes and Distribution and Logistics Networks.
Manufacturing and Assembly Processes involve several stages, including stamping, welding, painting, and the final assembly. The entire automotive supply chain, from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to multiple tiers, needs a fundamental restructuring due to the imbalance between risk and cost.
Distribution and Logistics Networks forms a complex web of various transportation modes, warehousing facilities, and inventory management systems. Implementation of Just-in-time (JIT) and lean manufacturing principles require meticulous coordination and synchronization of logistics operations. The interdependencies on multiple stakeholders can lead to production delays. The Automotive Logistics Global 100 report stated that the global automotive logistics market reached a total value of $241.7 billion in 2021 and is likely to reach $433.6 Billion by 2031. Thus, the optimization of distribution and logistics networks is not merely a financial consideration but a strategic imperative.

Current Supply Chain Landscape in the Automotive Industry
COVID-19 and Geopolitical Tensions
The COVID-19 crisis, post-pandemic effects, and geopolitical tensions worldwide have exposed weak supply chains. Such events have also highlighted the national security implications of supply chain vulnerability. The temporary shutdown of manufacturing plants, global logistics disruptions, and reduced consumer demand resulted in a sharp decline in automotive production and sales. According to the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers (OICA), global car production has declined by 16% in 2020 – compared to 2019.
Geo-political tensions that continue to reshape production and assembly processes have undermined the automotive industry. The traditional “just-in-time” (JIT) supply-chain model has buckled under the strain of unprecedented demand in the last few years. Tariffs, import/export restrictions, and retaliatory measures have impeded the flow of car parts across borders. For instance, the trade conflict between China and the US resulted in tariffs on several automotive products, including vehicles and parts. This increased supply chain complexity has forced companies to rethink their manufacturing approach and sourcing decisions.
Microchip Scarcity, Raw Material Constraints, and Price Fluctuations
The global shortage of microchips has affected the automotive industry, causing delays. Auto suppliers face many issues, such as material scarcity, increased lead times, high operational costs, and labor shortages. The automotive industry depends on various raw materials, including steel, aluminum, rubber, plastics, etc. Limitations in the availability of these materials pose auto supply chain issues. This has led to instability in material prices.
Automotive Industry Outlook Supply Chain in 2030

Unveiling Automotive Industry Supply Chain Challenges
Poor Routing of Parts Delays Automobile Manufacturing
On average, vehicles consist of approximately 30,000 individual parts, either produced internally or sourced from a third-party provider. If there is a minor disruption in any part of the supply chain, it can slow down the manufacturing and distribution of crucial components, resulting in the suspension of the production line. The move of automobile builders and brands towards just-in-time manufacturing by automobile builders and brands necessitates smooth construction and distribution of vehicles. Any disruption or inefficiency in this process means inventory shortages and revenue loss. Therefore, it is vital for automotive supply chain managers to effectively collaborate with manufacturers and suppliers to optimize parts manufacturing and streamline distribution.
Lack of Visibility and High Costs Impacts Profitability
Lack of visibility and high fixed and variable costs throughout the supply chain impacts profitability for automotive manufacturers. The costs involved in the automotive industry include investments in machinery, production lines, and automation, as well as high staff salaries due to technical skillset. Additionally, retirement and pension provisions for employees and research and development impact profitability. Commodity costs for purchasing aluminum, fabrics, steel, rubber, etc., contribute to the overall expenses. Moreover, third-party costs from automotive suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers directly affect price points and profit margins. Therefore, automotive manufacturers must gain visibility into fixed and variable costs to drive profitability.
Manufacturing Quality Control Issues
Automotive manufacturers bear the responsibility of delivering products of exceptional quality. However, even a single misstep or a lapse in oversight and auditing within the supply chain can have profound repercussions on product quality. Such lapses can result in vehicles failing to meet performance expectations, which, in turn, tarnishes the reputation of automotive manufacturers. Additionally, it leads to material wastage, hampers revenue generation, triggers operational inefficiencies, and elevates costs.
Recent studies have underlined a concerning trend: a notable increase in high-profile automotive recalls in recent years. These recalls have exacted a significant financial toll on industry leaders, not only damaging their brand reputation and revenue but also affecting the overall quality and performance of automotive vehicles and their components. Such compromises in quality and performance can pose serious risks to drivers, making it a critical concern within the automotive supply chain.
Poor Communication and Collaboration
A multi-tiered network (suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors) in the automotive supply chain creates communication challenges due to the inherent complexity and sheer volume of interactions. A dearth of collaboration can give rise to challenges concerning data integration, real-time information exchange, and interoperability. These issues, in turn, can trigger production and delivery delays, ultimately resulting in extended lead times, missed deadlines, and, ultimately, customer dissatisfaction. The availability of timely and precise information to any party within this network is pivotal as it fosters collaboration and informs sound decision-making.
Lack of Resilience
The automotive industry remains highly vulnerable to disruptions stemming from a variety of sources, including natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and unforeseen events. Compounding these challenges are issues related to inadequate inventory management, limited operational visibility, insufficient communication and collaboration, as well as the persistent reliance on outdated technologies and manual processes. These factors collectively undermine the resilience of the automotive supply chain, rendering it less capable of effectively responding to and recovering from disruptions.
Automotive Supply Chain Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
To navigate the complexities and interdependencies inherent in the automotive industry, companies must prioritize investing in highly efficient and risk-optimized systems while embracing industry best practices. With Quloi’s supply chain visibility software, organizations can gain real-time insights that empowers them to optimize inventory levels, forecast demand accurately, and proactively identify potential bottlenecks or risks within their supply chain.
Effective Risk Management
Effective risk management in the automotive industry involves thorough risk identification to anticipate potential issues in the supply chain. Manufacturers can minimize disruptions by developing contingency plans and implementing risk mitigation measures. This can include backup manufacturing capabilities, alternative logistics providers, and consideration of operational relocation for tariff advantages. Through proactive risk management, the automotive sector can build a resilient supply chain.
Digitalization and Collaboration
By leveraging interconnectivity and instrumentation, supply chain firms can tap into comprehensive consumer insights and improve both products and supply chain operations based on consumer preferences. Historically, consumer information was primarily concentrated among dealers and service/repair shops, with limited access for OEMs and suppliers. However, by adopting smart supply chain practices and digitalization, processes can be transformed, enabling seamless sharing of information across the entire supply chain network. This collaborative approach facilitates agility and adaptability, ultimately leading to more responsive and customer-centric operations.
Quality Reporting and Visibility
Quality Reporting and Visibility: Network-connected smart sensors enable real-time parts tracking to ensure stringent quality control. These sensors provide objective data on indicators such as location, temperature, and humidity inside shipping containers or trucks. This capability allows organizations to identify and isolate parts shipments affected by quality breaches, reducing the risk of costly recalls. External audits of suppliers and manufacturers, as well as batch control implementation, help organizations adhere to quality standards and identify potential sources of faulty parts.
Data-Driven Decision Making
By leveraging technology and harnessing data from sensors, IoT devices, GPS, and RFID tags, supply chain firms can gather accurate and timely information about goods as they move through the supply chain. Real-time visibility enables proactive identification and resolution of bottlenecks, ensuring highly effective and reliable supply chain operations. Data-driven insights help mitigate the risk of stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and optimize supply chain processes. As a result, it leads to improved OTIF performance and overall efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing supply chain issues in automotive industry requires combining technological solutions, collaboration, and strategic approaches. Quloi’s ScaaS solution offers valuable insights and real-time visibility, enabling organizations to track shipments, monitor performance, and identify bottlenecks. This leads to improved operational efficiency and reduced lead times.
Quloi facilitates seamless communication and information sharing, allowing for better alignment and anticipating demand fluctuations. With data-driven decision-making and a focus on continuous improvement, automotive organizations can optimize their supply chains and thrive in a dynamic industry. Book a Demo to learn how Quloi helps organizations navigate challenges and build a more efficient and resilient automotive supply chain.
FAQs
What is automotive supply chain optimization?
Automotive supply chain optimization maximizes efficiency and performance by improving delivery times, collaborating, diversifying the supplier base, minimizing costs, and streamlining overall operations.
Which supply chain trends are disrupting the automotive industry?
Automation, Digitization, and advanced tech-driven business models have transformed other industries, and automotive will be no exception. The disruptive forces in the auto industry include autonomous driving, mobility solutions, electric vehicles, connectivity, and sustainability.
What are the challenges faced by automotive supply chains?
The auto industry is challenged by changing customer expectations, increased lead times and operational costs, and adopting new technologies like EVs. Limitations in the availability of raw materials make it difficult to match customer expectations, posing auto supply chain issues.
