Optimizing the Oil & Gas Supply Chain with Digitalization
Climate change is no longer a distant threat, and humanity is struggling with its effects and taking action in all parts of the economy. As part of global efforts to mitigate its effects, transitioning to a lower-carbon energy system is imperative. The transition demands fundamental shifts in how energy is produced, distributed, and consumed worldwide. Such shifts call for strategic and proactive responses from businesses.
The oil and gas industry is no exception, where fossil-sourced products influence the energy-supply outlook. Volatile costs and labor and material-supply uncertainties pose significant risks to field operations and project delivery. This blog will explore some of the most common challenges in the oil and gas industry and how digitalization can help overcome them when used effectively.
Oil and Gas Supply Chain Explained
The oil and gas (O&G) industry is one of the world’s largest and most influential sectors. However, it is also extremely volatile. It operates a global supply chain in challenging geographic and climate conditions. The industry faces monumental challenges that threaten its stability.
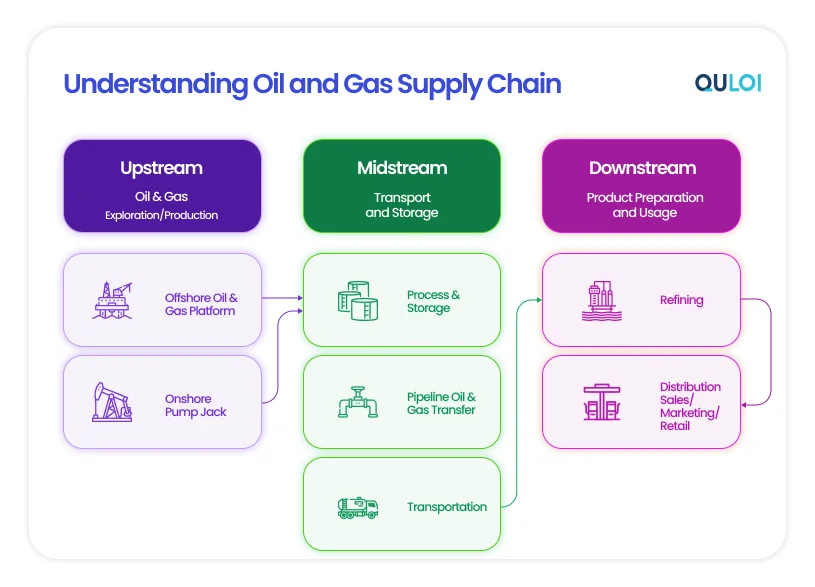
The supply chain in O&G falls into three segments: upstream, midstream, and downstream. The industry’s primary goal is to ensure that materials, products, and equipment reach their destination on time and in full. Given its dynamic nature, the industry requires efficient supply chain management and responsibility to function properly. This puts oil and gas players’ traditional business models under the pressure of high-quality maintenance and adaptability.
Apart from traditional challenges like oil pricing volatility, which creates an imbalance between demand and supply, there are a few other significant challenges. Let’s dive in!
Challenges in Managing Oil and Gas Supply Chain
Price Volatility
Cost overruns and fluctuations in oil prices negatively impact global oil producers, disrupting the entire supply chain. When oil prices drop, companies reduce production, increasing lead times and supply shortages. A Deloitte study cited that OPEC+ (a group of oil-producing countries) decided to cut their oil production by 2.5 million barrels per day, resulting in a shortage of oil supply. This reduction in supply pushed the price of Brent oil above $90 per barrel. On the contrary, operational costs increase when prices rise and profits take a downturn.
Geopolitical Risks
The oil and gas sector contends with geopolitical uncertainties and demand shocks, which can lower production efficiency. Conflicts and regulatory changes may halt production or restrict access to key resources, causing delays and increased costs.
For instance, recent tensions in the Middle East have heightened concerns about potential disruptions to global oil supplies. The latest report speculates how oil and gas prices react to geopolitical tensions. These disruptions can have cascading effects throughout the supply chain, impacting everything from drilling operations to refinery production.


Demand-Supply Imbalance
Inaccurate demand forecasts can cause a bullwhip effect. Fluctuations in demand and supply can result in overproduction or shortages. Underproduction can lead to supply shortages and lost revenue, while excess inventory costs can result from overproduction.
For instance, in the 1990s, Volvo’s consumer operations, a world-leading truck brand, faced a massive inventory of green-colored cars. With excess inventory on shelves, Volvo began offering these cars at a steep discount. However, upstream, the manufacturing elements of the supply chain only saw a surge in sales. Assuming high demand for the green model, they produced more green cars. A single inaccurate forecast can intensify the bullwhip effect in the oil and gas industry, causing upstream supply chain members to interpret a 10% shift in point-of-sale demand as an up to 80% shift in overall demand.
Logistical Challenges
The vast distances and often unforgiving environments associated with oil and gas operations present unique logistical hurdles. Harsh weather conditions in the Arctic or deepwater offshore drilling rigs can significantly impede essential equipment and supply movement. Furthermore, complex regulations, like those governing the transport of liquefied natural gas (LNG), add another layer of complexity to the logistical equation. Disruptions like the recent Red Sea vessel attacks by Houthi rebels highlight the vulnerability of global supply chains. Such incidents can cause cascading delays and increase costs, as carriers are forced to reroute shipments, impacting industries beyond oil and gas, as exemplified by the delays experienced by shippers like Ikea. Real-time data visibility throughout the supply chain is crucial for mitigating these disruptions and ensuring efficient operations.
Environmental Regulations
The oil and gas industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint. Environmental regulations, such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) 2020 sulfur cap, force companies to adopt cleaner technologies and practices. The IMO 2020 regulation, for example, mandates that ships use lower-sulfur fuel oil, which reduces air pollution. These regulations add complexity to the supply chain and require companies to find new ways to operate more sustainably. In early 2024, the global oil and gas industry saw a 45% decline in the number of times companies mentioned environmental sustainability in their official filings compared to the previous quarter. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal repercussions, and reputational damage.
Technological Integration
Traditional players that do not digitalize their oil and gas supply chains lag behind others. The lack of data standardization and data sharing due to non-integrated systems can create data silos and fragmentation. This fragmentation obstructs the flow of valuable insights, hindering effective decision-making. Integrating technologies like ERPs and key supply chain players, such as shippers and custom brokers, can break down these data silos and foster greater collaboration. These solutions enable real-time data sharing across the supply chain, allowing all players to make informed decisions based on accurate information.
Shifting Gears to Supply Chain Digitalization
The oil and gas sector has always been a story of boom and bust, but digitization has emerged as a game changer. As global competitive pressures rise and profit pools shift, supply chain digitalization will provide more long-term security to an industry that previously had blindly ducked the dips.
Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, artificial intelligence, automation, supply chain traceability, and blockchain are promising solutions that could streamline oil and gas supply chains, ensuring cost control and increased operational efficiency. A Deloitte report states that generative AI could enhance process efficiency by integrating and analyzing diverse data sources. It can help process large data volumes proficiently to optimize operations, resulting in cost reduction and revenue expansion.

The digital oil and gas supply chain focuses on cost, efficiency, and speed. It allows buyers and suppliers to digitize and access all records in a centralized repository. Digitized data can be routed to various platforms to enhance production efficiency and make real-time, informed decisions. Companies prioritizing digitalizing their oil and gas supply chains will be well-positioned to meet their industry’s challenges. Since technology is readily available and proves its value by reducing costs and increasing efficiency, digitalization could create the difference between leading the next wave of industry innovation and lagging.
Thinking Big, Scaling Fast with Quloi
Investing in digital technologies is a no-regret move for oil and gas companies to remain resilient and competitive in this evolving landscape.
Collaboration: The Quloi platform fosters collaboration between buyers and suppliers by allowing them to engage in group chats, access system-generated notifications, undertake approval actions, invite users to join the conversation, and share necessary documents.
Visibility: The Quloi platform provides visibility into shipment movements and delivery statuses, facilitating proactive management of logistics operations and ensuring on-time deliveries.
Track Modifications: The platform automatically generates notifications for order changes, and a dedicated chat history tracks all communication and updates regarding each order item modification, ensuring clear communication with the supplier.
Scalability and Flexibility: As a cloud-based solution, the SaaS platform supports seamless integration with Slack and Microsoft Teams. This integration facilitates seamless communication and real-time data sharing.
To stay ahead of the curve in the power value chain, Book a demo and discover the potential of a cloud-driven supply chain visibility and collaboration platform.