Understanding Challenges in Paper Supply Chain
Paper is everywhere, from the books we flip through at a library to the cardboard boxes that deliver our online shopping. It wraps the sandwiches we take on the go and even insulates the walls of our homes. Whether it’s a notebook we jot down ideas in or the labels on our medicines, paper production relies on a well-managed supply chain.
While paper may seem like an everyday object, its journey from forest to consumer involves a surprisingly intricate supply chain. This multi-tiered system, encompassing everything from pulp production to printing and writing paper, is vital for global distribution and fulfillment. However, the industry faces a growing list of challenges that threaten to disrupt this delicate balance. This blog dives into the pulp and paper world, exploring the key trends and the significant challenges that threaten the industry’s efficiency, sustainability, and profitability.
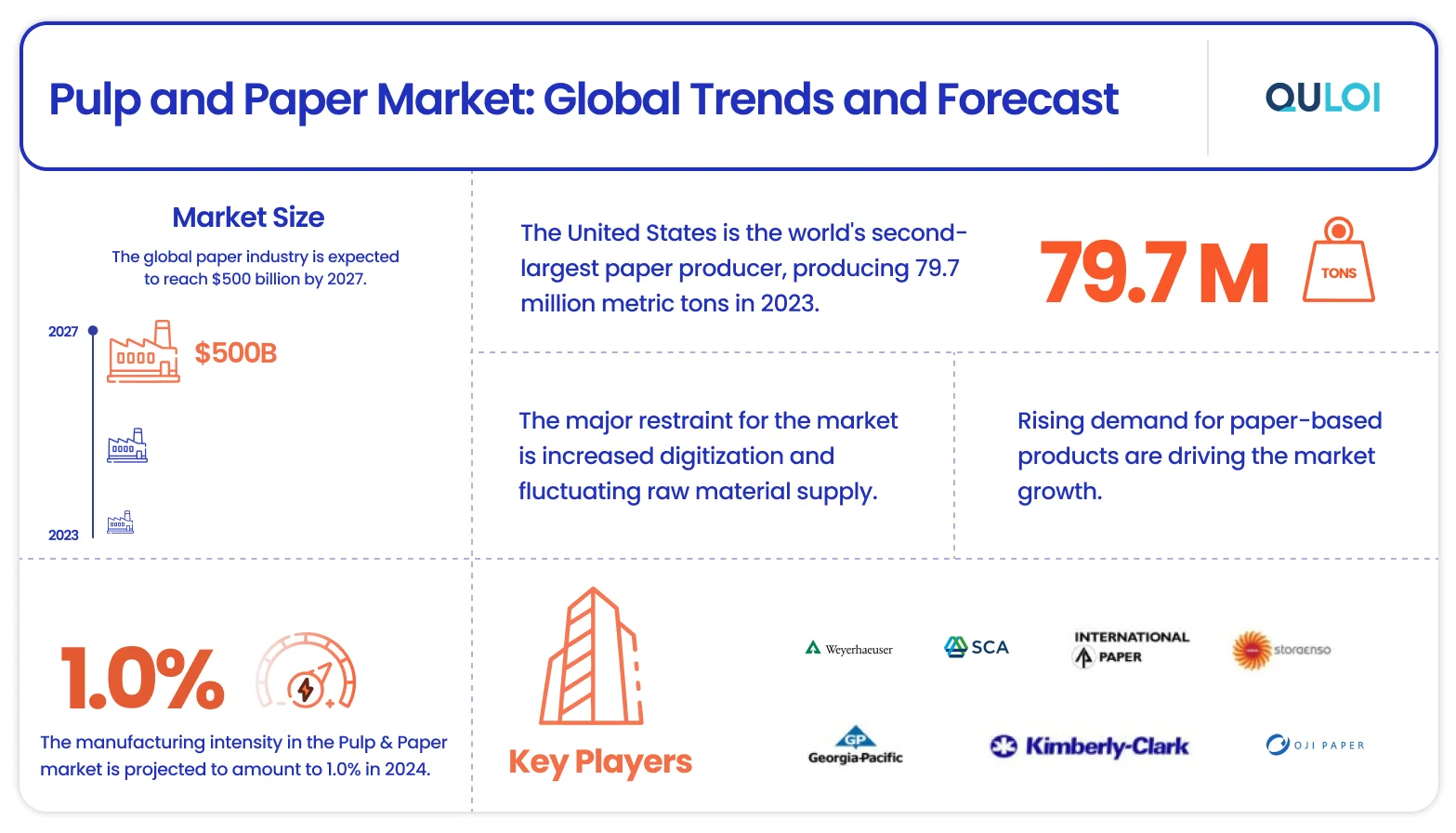
Supply Chain Challenges Facing the Paper Industry
The pulp and paper industry is a significant player in the global landscape, with high water usage, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions. While the industry has made notable advancements, supply chain issues have thrown curveballs in its distribution and fulfillment operations. From labor shortages to production decline and a hike in market prices, the industry experienced a whirlwind of change. Here are some of the most pressing issues and challenges facing the paper supply chain:
Raw Material Volatility
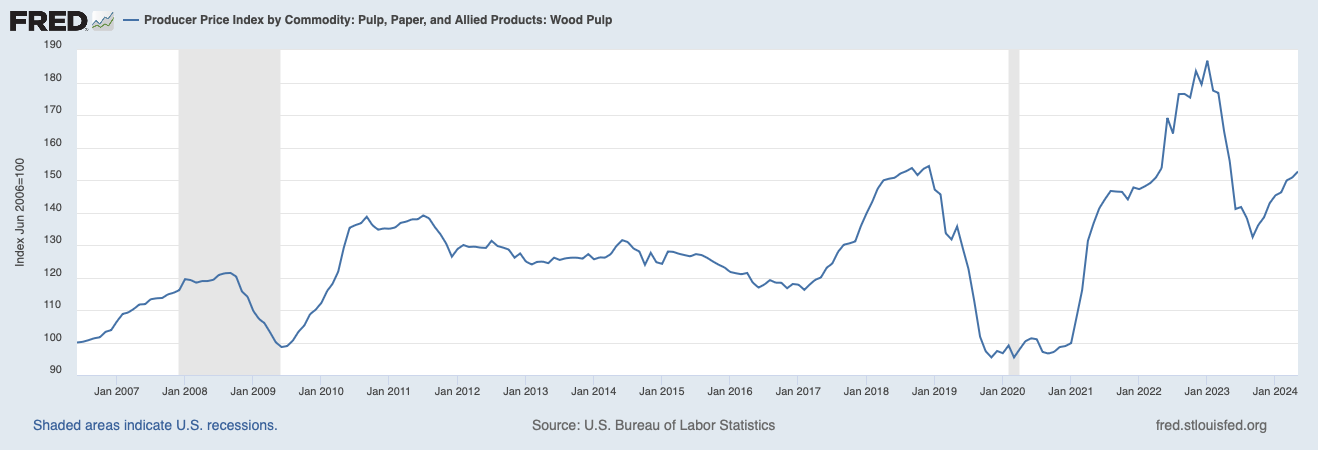
The demand for pulp, the primary raw material for paper, is susceptible to price fluctuations due to weather, disease outbreaks, or changes in land use. A report published by Federal Reserve Bank shows fluctuations in pulp and paper, and allied products. This volatility makes it difficult for paper manufacturers to maintain stable pricing. Balancing the demand for wood fiber with sustainable forestry practices is also important. Overharvesting of trees can lead to resource destruction and habitat loss. Environmental regulations like meeting FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certification add raw material sourcing costs.
Logistics and Transportation
Paper products are heavy and sensitive to temperature and moisture. Transporting massive volumes of paper products requires specialized logistics based on various (distance, reliability, speed, availability, cost, and environmental impact) to prevent damage, avoid delays, and minimize costs. According to CNN Business, businesses spent $1,920 to book a 40-foot steel container for shipping. At the same time, with the pandemic outbreak, companies paid about $14,000 for the same shipping container – a dramatic 600% increase to ensure timely delivery. Paper products must also be stored in specific conditions to maintain optimal humidity levels and prevent rapid deterioration. This, in turn, leads to increased storage costs.
Limited Visibility
Ensuring real-time visibility into supplier processes, inventory schedules, and delivery schedules can lead to operational inefficiencies and higher costs. Integrating data from disparate sources into a unified view remains challenging, hindering decision-making and responsiveness. For example, a paper manufacturer needs real-time updates on the availability of wood fiber from its suppliers to schedule production efficiently. Without accurate visibility, they may face inventory shortages or overstocking.
Supplier Reliability
Depending on a limited number of suppliers for raw materials can pose significant issues. If a key supplier faces production delays or logistical problems, it can disrupt the entire supply chain. Manufacturers may face the risk of variability in the performance of raw materials. Fluctuations in quality can affect product standards, declining sales, and resulting in poor supplier management.
Environmental Concerns
As the second-largest consumer of paper and paperboard worldwide, the US consumed approximately 65.76 million metric tons of paper and paperboard in 2022. Paper manufacturing is water- and energy-intensive, particularly in the drying and refining stages. The US benchmark for water consumption within pulp and paper mills is around 17,000 gallons/ton of paper, with one of the most efficient kraft pulp and paper mills only consuming 4,500 gallons/ton. The more paper is produced, the more natural resources are consumed. This becomes challenging as it leads to a significant carbon footprint from the source to the end product and results in higher operational costs.
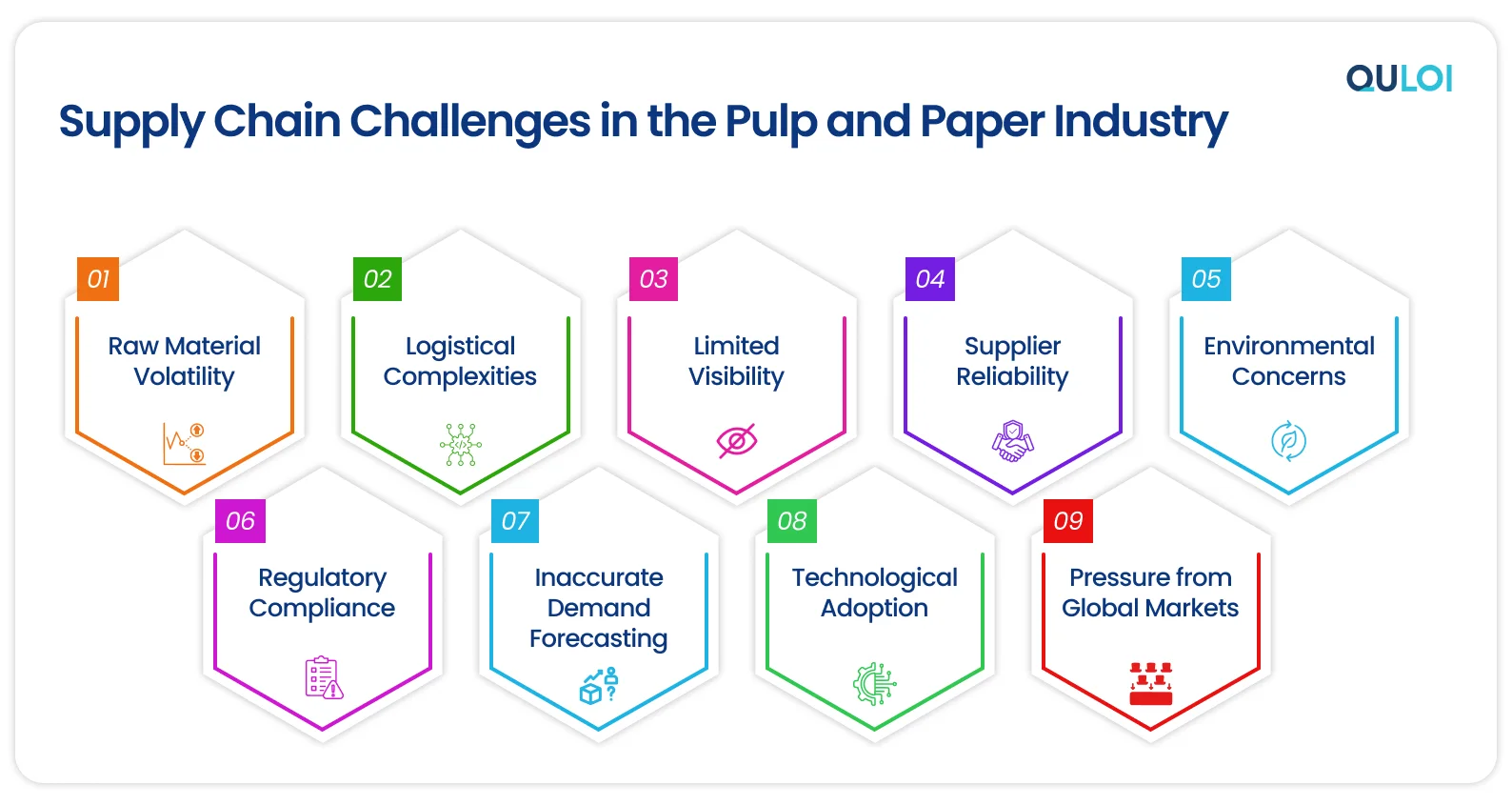
Regulatory Compliance
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration of the U.S. Department of Labor) has enforced specific standards for human health and environmental safety in the paper industry in the U.S. During paper processing. multiple chemicals and dust can become highly concentrated in the air – posing threats to human health and the environment. Not adhering to product standards regarding emissions, waste disposal, and sustainable forestry practices and certifications (e.g., FSC, PEFC) can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
Demand Dynamics
Forecasting accurate customer demand for different paper products can be challenging, leading to poor inventory management and bullwhip effect in the supply chain. Due to seasonal fluctuations, changing market trends, and evolving customer preferences, balancing inventory levels without incurring high storage costs or obsolescence is a constant battle.
Technological Adoption
Adopting new technologies is promising but comes with substantial costs and the need for skilled personnel. Most manufacturers still rely on different systems that may not be integrated with modern supply chain management tools, leading to issues in data sharing, timely communication, and document management. For instance, most of the time, produced items wait in the warehouses, either in the port of discharge or the port of loading, due to improper communication and poor visibility.
Increased Global Competition
The paper industry has evolved into a globalized marketplace, with competition from manufacturers in countries with lower labor costs or lax regulatory standards. This global competition pressures domestic producers to reduce operational costs or specialize in niche markets to maintain competitiveness. Also, political instability and trade wars can disrupt the flow of raw materials and finished paper products. As a result, manufacturers may face shortages, price hikes, and difficulty fulfilling customer orders.
How Can a SaaS Supply Chain Visibility Platform Help?
Understanding market dynamics and customer preferences is paramount for success in the fiercely competitive pulp and paper industry. From raw material sourcing to balancing demand swings and competition, the challenges faced by this industry are diverse. However, Quloi, a cloud-driven supply chain visibility and collaboration platform, helps you scale your paper supply chain growth by enabling end-to-end visibility, centralizing data and communication channels, and streamlining supplier management.
Read the blog in next series to learn how paper manufacturers can navigate global challenges more effectively while gaining a competitive foot in the industry.
Interested to learn more? Book a FREE Demo!
Related Articles


